Optical Fiber Splice Loss
Definition
Fusion splicing is a technique to join two fibers ends. Optical power loss at the splicing point is known as splice loss.
How splice loss can be measured?
An Optical Time Domain Reflectometer (OTDR) can be used for splice loss measurement. A cable section-containing splices are normally shown as knees on the optical power loss OTDR graph. As per the procedure (ANSI/TIA/EIA-455-8-2000), splice loss measurements with an OTDR must be conducted from both directions and averaged (by adding with signs)for accurate splice loss. Below is the graphical picture of ‘gainers’ and ‘exaggerated losses’ measurements; the effect on actual splice loss is relatively low.
It is important to remember that actual splice-loss is the measured splice-loss in both directions divided with two.
On which parameters splice loss is dependent?
The parameters, which control loss in any fiber joining method, can be classified as Intrinsic and Extrinsic parameters.
Intrinsic Parameters
Intrinsic or fiber related parameters are determined when the fiber is manufactured and cannot be controlled by the individual doing splicing.
Mode Field Diameter (MFD) is the most important intrinsic parameter. More splice loss can be observed for higher difference in MFD values. The MFD is a characteristic, which describes the mode field (cross-sectional area of light) traveling down a fiber at a given wavelength. When fibers with different MFD values are spliced together, a MFD mismatch occurs at splice point. With the help of the following formula splice loss due to MFD mismatch can be calculated from MFDs (in Em) of two fibers.
MFD of PMD-LITE fibers can vary from 8.8 to 9.6 Em. As per the above equation splice loss between two extreme MFD values is 0.035 dB.
Extrinsic Parameters
Extrinsic, or splice process related parameters are those induced by splicing methods and procedures. Splice process parameters include lateral and angular alignment, contamination at the fiber end and core deformation due to un-optimized heating & pressing. These external parameters can be controlled/minimized by improving skill of the individual doing splicing and by automated fiber alignment and fusion cycles.
It has been observed that splice loss between two identical fibers with same MFD and geometry parameters is as high as 0.04 dB. This excess loss is due to miss alignment and other splicing process parameters. Figure 3 shows fiber end conditions with various unoptimized splicing parameters.
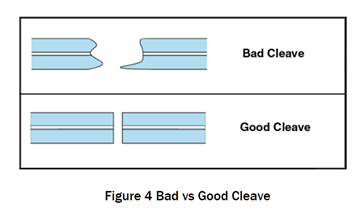
Other important extrinsic parameter is fiber end angle. Proper fiber end preparation is the most fundamental step to get acceptable splice loss. Generally end angle less than two degrees gives acceptable field splice loss. End angle is dependent on condition of cleaver and cleaver blade. Typical end angle of well – maintained cleaver is around one-half degree. Figure4 is showing comparison between bad and good cleaving. It has been observed that extrinsic parameters can give splice loss as high as 0.4 dB. By controlling extrinsic parameters, acceptable field splice loss can be achieved.
Recommended Splicing parameters for Sterlite’s G652 fibers
Parameters
• ARC duration 01.50sec
• Pre-fusion 00.10sec
• ARC gap 10.00μm
• Overlap 15.00μm
• ARC power 00.20step
Alignment method
• Auto Core Alignment
Fiber end check
• Auto cleave angle check
Measurement method
• Optical time domain reflectormeter (discussed above)