VCSEL Laser – The Advantages of VCSEL

What is VCSEL?
VCSEL stands for Vertical-Cavity Surface-Emitting Laser. It is a type of semiconductor laser diode with laser beam emission perpendicular from the top surface, contrary to conventional edge-emitting semiconductor lasers which emit from surfaces formed by cleaving the individual chip out of a wafer.
Advantages of VCSEL laser
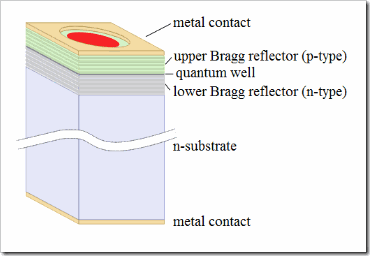
A typical VCSEL consists of two oppositely-doped distributed Bragg reflectors (DBR) with a cavity layer between. In the center of the cavity layer resides an active region, consisting of multiple quantum wells. Current is injected into the active region via a current guiding structure either provided by an oxide aperture or proton-implanted surroundings. As the entire cavity can be grown with one-step epitaxy, these lasers can be manufactured and test on a wafer scale. This presents a significant manufacturing advantage.
The VCSEL cavity is very short, 100-1000 times shorter than that of a typical edge-emitting laser. There is typically only one Fabry-Perot(FP) wavelength within the gain spectrum; hence the FP wavelength(and not the gain peak) determines the lasing wavelength. The optical thickness variation of the layers in a VCSEL changes the lasing wavelength. The position of the layers with thickness variation to the center of the cavity is crucial for the resulting wavelength variation; the closer they are to the cavity center, the larger the wavelength change. This property lends to simple designs of wavelength-tunable VCSEL and multiple wavelength VCSEL arrays.
The VCSEL is, today, an established light source for data transmission in short-distance links, interconnects, and local networks (LANs, SANS, etc.). In these applications, the VCSEL is on-off modulated for the transmission of digital signals. Recent work on analog modulation of VCSELs indicates that VCSELs are suitable light sources also for the transmission of RF and microwave signals in, e.g., radio-over-fiber (RoF) networks used in antenna remoting in cellular systems for mobile communication.
Common to all these applications is that they put certain requirements on the high-speed modulation performance. With higher data rates and modulation frequencies, the requirements become more demanding and it becomes more difficult to identify VCSEL designs that fulfill the requirements.